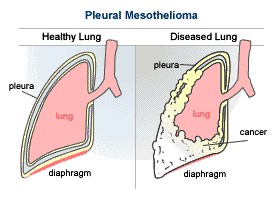
Mesothelioma Cancer Research and Clinical Studies
Mesothelioma Cancer Research Study #1:
“Solitary (localized) pleural mesothelioma: A light- and electron-microscopic study”
in American Journal of Surgical Pathology
Abstract – Six solitary (localized) pleural mesotheliomas were studied by light and electron microscopy. All the lesions were benign and were composed mainly of fibrous tissue of variable cellularity with or without cystic spaces lined by round cells. The lining cells of the cysts and the adjoining round plump cells were interpreted as true neoplastic cells of the fibroblast type. Results of light- and electron-microscopic study of human mesothelial cells and fetal mesothelial cells of rats were compared. The cytoplasmic organelles of the tumor cells were generally scanty, though rough endoplasmic reticulum, sparse mitochondria, intracellular bundles of fibrils, and numerous polysomes were seen.
Some tumor cells had junctional apparatus and basement membranes and showed inter-digitation of the plasma membrane. These cells lined the cystic spaces irregularly and also proliferated into the surrounding fibrous tissue, where they assumed a spindle shape and resembled fibroblasts. Ultra structurally, the tumor cells were similar to mesothelial and stromal cells of fetal rat pleura. We speculated that the solitary (localized) mesotheliomas were probably derived from coelomic epithelium and that tumor cells remained un-differentiated or revealed minimal differentiation toward mesothelial cells.
Mesothelioma Cancer Research Study #2
“Reactivity of six antibodies in effusions of mesothelioma, adenocarcinoma and mesotheliosis: stepwise logistic regression analysis”
in Cytopathology Volume 11, Issue 1, Feb 2000
Abstract – Anti-CEA, anti-vimentin, CAM5.2, BerEp4, Leu-M1 and anti-EMA were applied to effusions from 36 mesotheliomas, 53 adenocarcinomas and 24 reactive mesothelial proliferations.
Stepwise logistic regression analysis selected three criteria of major importance for distinguishing between adenocarcinoma and mesothelioma: BerEp4, CEA and EMA accentuated at the cell membrane (mEMA), these three being of similar diagnostic value. The pattern BerEp4−, CEA− and mEMA+ was fully predictive for mesothelioma (sensitivity 47%), whereas the opposite pattern was fully predictive for adenocarcinoma (sensitivity 80%). Only EMA seemed to distinguish between mesotheliosis and mesothelioma. Comparison of reactivity in cytological and histological material from the same mesotheliomas showed similar staining frequencies for CEA and CAM5.2, with some random variation for Leu-M1 and EMA, whereas vimentin and BerEp4 reactivity was more frequent in cytological specimens.
Mesothelioma Cancer Research Study #3
“A pilot study of systemic corticosteroid administration in conjunction with intrapleural adenoviral vector administration in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma”
– Sterman DH, Molnar-Kimber K, Iyengar T, Chang M, Lanuti M, Amin KM, Pierce BK, Kang E, Treat J, Recio A, Litzky L, Wilson JM, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM. – Cancer Gene Ther. 2000 Dec;7(12):1511-8.
Abstract – One of the primary limitations of adenoviral (Ad) -mediated gene therapy is the generation of anti-Ad inflammatory responses that can induce clinical toxicity and impair gene transfer efficacy. The effects of immunosuppression on these inflammatory responses, transgene expression, and toxicity have not yet been systematically examined in humans undergoing Ad-based gene therapy trials. We therefore conducted a pilot study investigating the use of systemic corticosteroids to mitigate antivector immune responses. In a previous phase I clinical trial, we demonstrated that Ad-mediated intrapleural delivery of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene (HSVtk) to patients with mesothelioma resulted in significant, but relatively superficial, HSVtk gene transfer and marked anti-Ad humoral and cellular immune responses. When a similar group of patients was treated with Ad.HSVtk and a brief course of corticosteroids, decreased clinical inflammatory responses were seen, but there was no demonstrable inhibition of anti -Ad antibody production or Ad-induced peripheral blood mononuclear cell activation. Corticosteroid administration also had no apparent effect on the presence of intratumoral gene transfer. Although limited by the small numbers of patients studied, our data suggest that systemic administration of steroids in the context of Ad-based gene delivery may limit acute clinical toxicity, but may not inhibit cellular and humoral responses to Ad vectors.